Purpose
The Escalations page provides several different sections presenting in a kanban format. This article provides guidance on what actions you can take within each column and what impacts those actions will have within SupportLogic.
Summary
Review the impacts of decisions made in the Escalations page and from working through the Escalation Workflow and what actions will and will not help train the Machine Learning engine of SupportLogic.
Escalation Page Kanban View
Within the Escalations page kanban view cases are segmented into five (5) different sections:
- Cases reviewed - groups reviewed cases by Acknowledged, Snoozed or Disagreed decisions that have been taken on cases (by anyone in your organization)
- Likely to Escalate - Machine Learning (ML) model prediction based on different LTE factors
- Escalation Requests - Signals extracted from customer comments
- Active Escalations - Cases escalated within customer CRM by the customer/agent
- Resolved Cases - Cases that were predicted to escalate but are now in the Closed or Resolved status

Next, let's look at the sections you need to take actions in.
Likely to Escalate
These are the cases which are processed by Machine learning and predicted for escalation. The support cases which may get escalated are predicted proactively and grouped based on 5 factors which leverage 25 different case meta data to predict cases that are likely to escalate. The groupings of the meta data are:
- High customer urgency
- Customer history
- Poor support responsiveness
- Case activity
- Case age
In the case of Likely To Escalate (LTE), the predictions are done directly from SupportLogic which allows us to perform below operations after that LTE cases clears the queue and moves into the respective columns under the Cases reviewed section.
Acknowledge (I took care of this case ) | Available |
Disagree ( Disagree with prediction ) | Available |
Snooze (Snooze this case) | Available |
Trains the ML model | Yes |

Escalation Requests
These are cases where customers or your internal company members have requested for an escalation. SupportLogic processes the case comments and it detects the request for escalation. On the Escalation page, cases with customers requesting escalations are shown under the Escalation Requests column.
Acknowledge | Available on the Support Hub/Case view |
| Disagree / decline | Available |
Snooze | Not Available |
| Trains the ML model | No |


You can also take direct action on the case and change the status to Escalated if you wish to confirm the customer's request to escalate a case.
Active Escalations
These are escalated cases directly updated from the CRM, the SupportLogic application shows the escalations based on the value in the CRM .
When the case is escalated, the is_escalated field in the CRM database will be changed as True. When the field changes it gets updated and the ticket is marked as Escalated in SupportLogic. These escalated cases show up in the list until the case is closed.
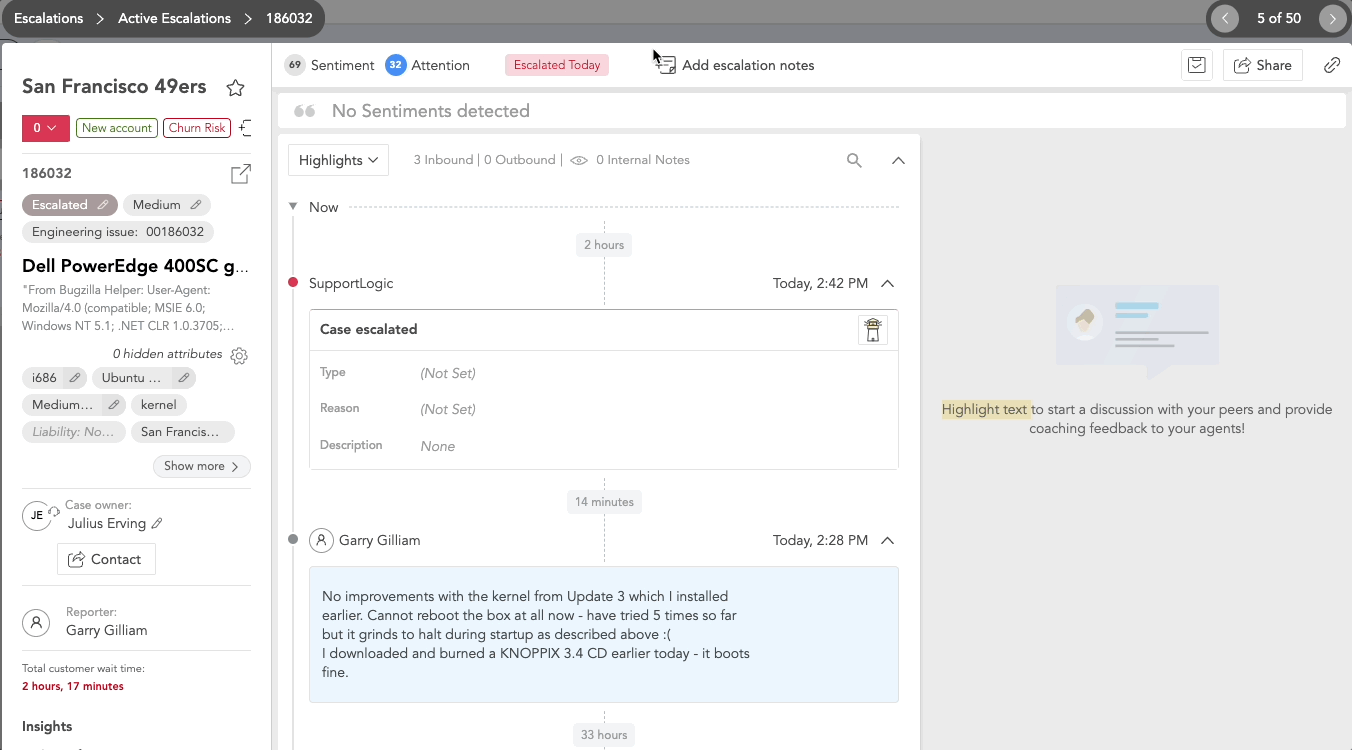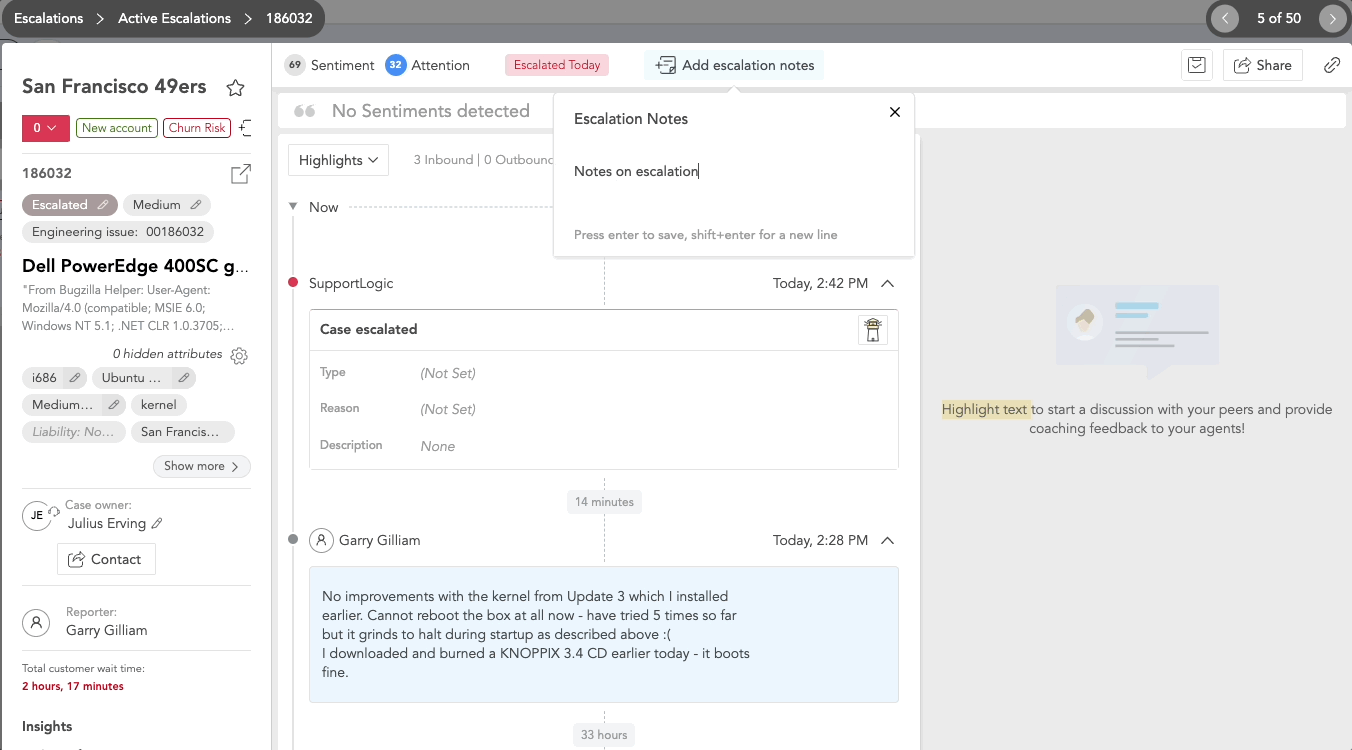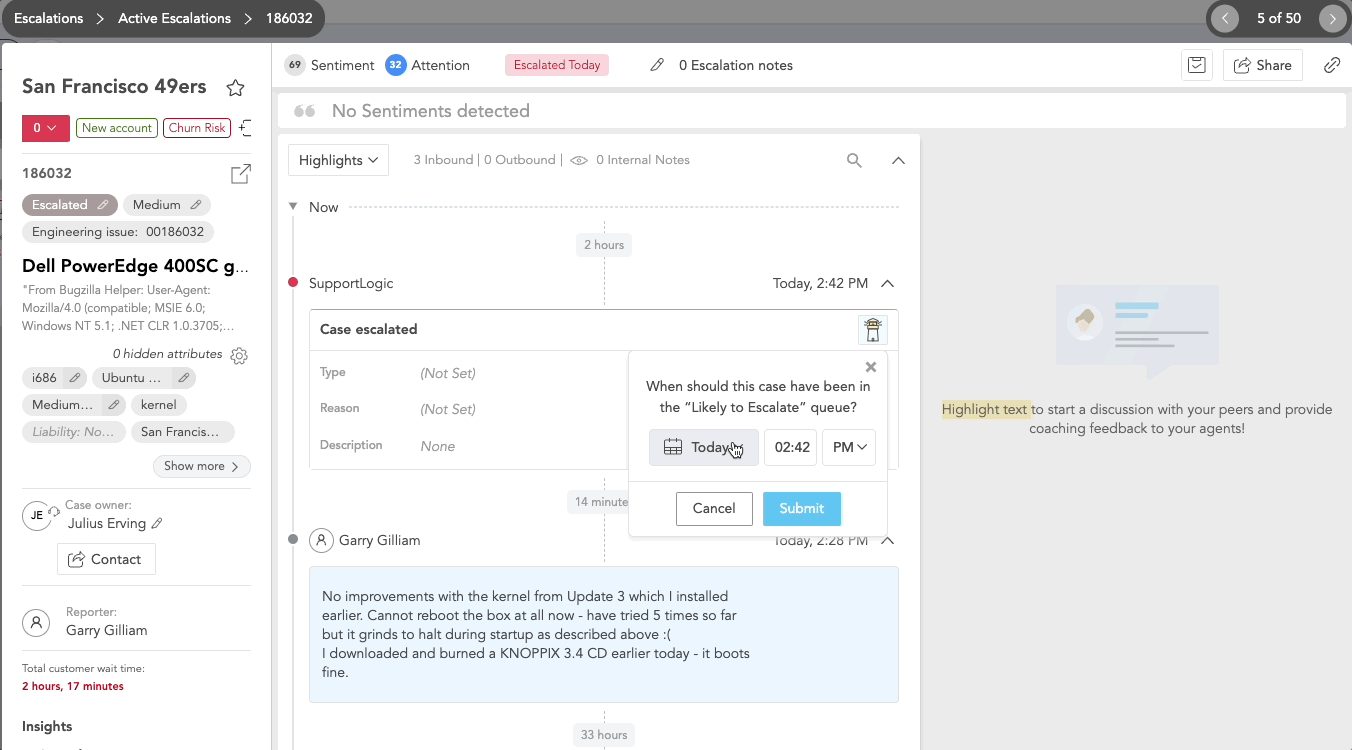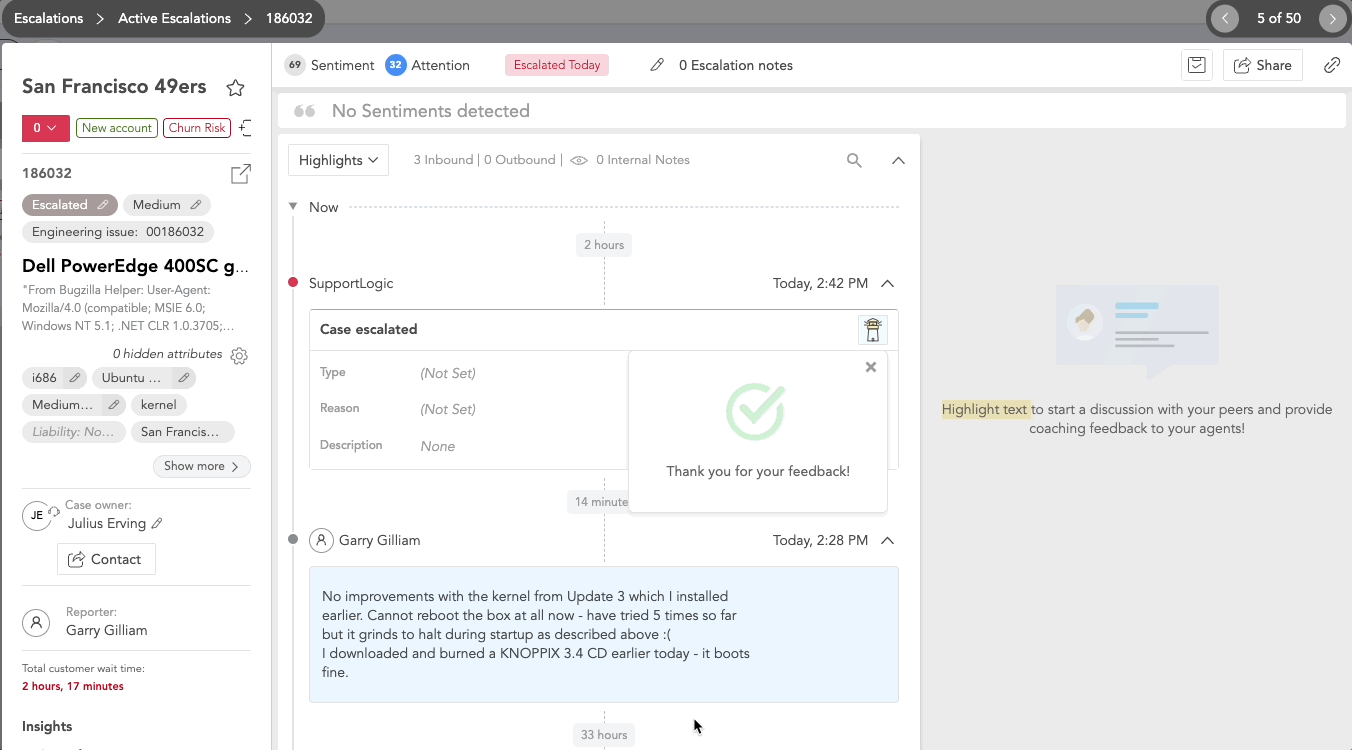
For Active Escalation cases you can:
- Add escalation notes for the users handling the case. These notes are visible only to the case owner and the user who added the note.
- Provide feedback to SupportLogic regarding the timing of the prediction of this case's escalation, by clicking on the lighthouse icon in the case history.
Acknowledge | Not Available |
| Disagree | Not Available |
Snooze | Not Available |
| Trains the ML model | No |
Permissions required
For Users to add notes, and take actions on the Escalations page will need specific permission. Admins with access to Manage Users can switch on/off the Manage Escalations toggle for the desired users. Review the User Permissions article for more detail.
Was this article helpful?
That’s Great!
Thank you for your feedback
Sorry! We couldn't be helpful
Thank you for your feedback
Feedback sent
We appreciate your effort and will try to fix the article